Cybersecurity testing: 4 best practices to ensure highly safe IT solutions
To my mind when transferring valuable data to the online environment, people are more concerned about their safety. According to IT Governance, in January 2020, the total number of leaked records reached 1.5 billion.
That’s why to take the leading positions in the IT market and provide end users with a reliable IT solution, companies put a great emphasis on its security.
In the article, I’ll tell you about the consequences users face with a poorly protected app, and what QA best practices do help launch the software with in-built cybersecurity.
The paramount role of cybersecurity in today’s IT world
People use apps for various activities — eShopping, eBanking, eLearning, etc. — and entrust their personal data. Here, cybersecurity comes to the fore to protect the private information of consumers, patients, and even organizations.
According to the IBM Report 2021, the average total cost of a data breach increased by $0.38 million and reached $4.24 million in 2021.
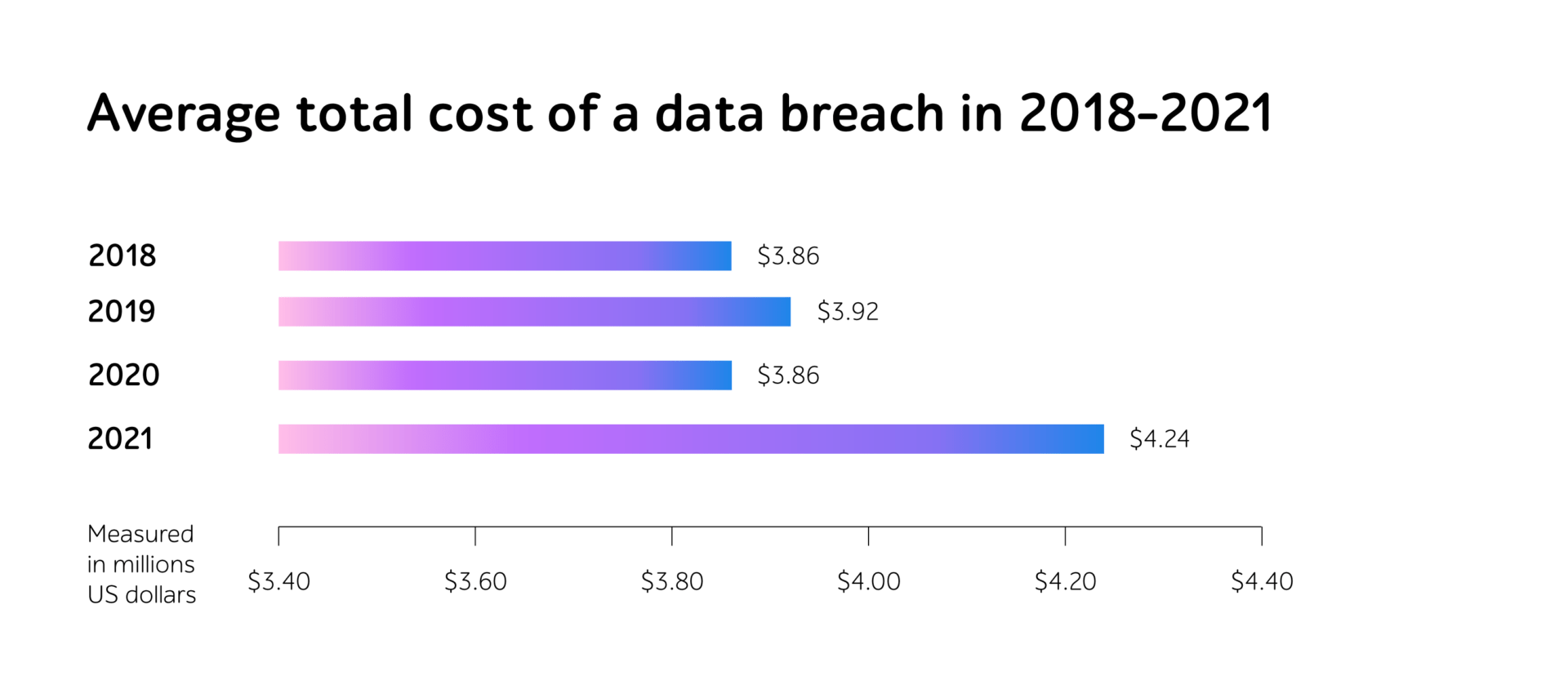
Source: IBM Report 2021
The research shows that only in the US, cyberattacks occur every 39 seconds. No doubt, businesses apply cybersecurity practices, reinforcing overall safety level, and watch out to avoid private data compromise.
When it comes to mobile apps safety, performing comprehensive cybersecurity testing is becoming a dire necessity. This allows protecting the IT solution from malware, phishing, and other malicious activities. Let’s have a look at the most common vulnerabilities if not:
- Data theft. If your software stores a voluminous amount of personal data without having enough cybersecurity measures, apps transmit the information to remote servers where hackers intercept it. Not a positive scenario for the day.
- Unauthorized access. When the developers rely on familiar encryption without strengthening or changing it, this makes the algorithms weak and vulnerable (and fraudsters gain access to user information).
- Session handling issues. Such challenges take place when the app allows the customers to perform transactions without logging or authenticating.
- Reverse engineering. Attackers introduce this technique to understand the app algorithms and structure while creating a malware program that performs the same functions, like a real one. Finally, this assists them in accessing the back-end servers.
- Client-side injection. Cybercriminals implement malicious code or send an infected link to end users, helping them reach some of the software functions.
4 mission-critical best practices to test mobile apps cybersecurity
When companies understand the problems that end users encounter, it becomes easier for them to build the right cybersecurity strategy to prevent further system penetration and data leakage.
Let’s take a look at the essential cybersecurity testing activities, helping increase the level of mobile apps safety.
1. Conducting penetration testing
I shall start with an example. You’ve probably heard that in 2021, hackers attacked LinkedIn and exposed 700 million users’ sensitive data on a darknet forum. It’s pretty much easier to prevent similar situations when introducing penetration testing, helping protect personal information, detect vulnerabilities, and ensure threat-resilient software.
How to conduct penetration testing to ensure that your software is attack-poof?
- Discover apps structure. Gather as much information about the software as possible (IT product architecture, source code, functions).
- Analyze software security. To assess whether the IT solution is vulnerable, QA engineers apply two methods: static analysis (by using the source code without installing the app) and dynamic analysis (by downloading it).
- Exploit flaws. Ethical hackers simulate cyberattacks to observe the system behavior, find vulnerabilities, and gain complete control over the software.
- Document results. The team creates a report on detected breaches, safety risks, and recommendations on fixing weak points.
2. Patching software on a regular basis
When a new vulnerability appears, it’s time to make a patch for the app to eliminate deficiencies. It also helps improve the apps performance and add changes to the functionality if needed. With more than 5.7 million mobile apps in App Store and Google Play, just imagine how many customers may become the victims of eCrime with no patches. By carefully testing them, businesses ensure that all software updates are secure and briskly react to flaws while mitigating cybersecurity risks, including sensitive data loss, ransomware attacks, insider threats, etc.
3. Adopting a DevSecOps approach
In the DevSecOps, the development cycles are short, helping identify and fix defects faster, reduce vulnerability risks, and provide software with embedded cybersecurity from the initial SDLC stages.
At the start of the project, DevSecOps allows considering possible security risks, which prevents critical issues at the development phase and reduces QA costs needed for subsequent fixes. Along with that, it provides a high level of IT solution protection and faster delivery to the market.
4. Performing pre-certification testing
To ensure that the app meets international and industry-specific regulations, such as HIPPA for eHealth, PCI DSS for eCommerce and BFSI, 3GPP for telecom, and many others, companies introduce pre-certification testing. It helps eliminate software inconsistencies with global standards of quality, cybersecurity, and data privacy, identify critical software issues, fix them, and get the product certified.
In order to guarantee the IT solution compliance with regulations, businesses undertake 4 essential steps of pre-certification testing:
- Analyzing technical requirements — assessing IT solution specifics to determine the core standards for compliance.
- Designing tests — defining the scope of QA activities, choosing the right tools, best practices, and creating test cases.
- Executing tests — running various scenarios to detect vulnerabilities.
- Reporting — documenting the results and describing non-compliant areas.
Closing remark
Just have a look: by performing thorough cybersecurity testing, it’s much easier to protect end-user personal data and prevent further system penetration. When building a QA strategy, we suggest including 4 cybersecurity best practices: performing penetration, patch, and pre-certification testing as well as introducing DevSecOps.
Feel free to contact a1qa’s experts to get professional support in enhancing your software cybersecurity.