Navigating the fintech frontier in 2024: QA’s role in delivering high-quality financial software
Over the past decade, the financial sector has undergone a remarkable evolution, driven by tech advancements and changing consumer behaviors.
As traditional banks pivot towards digitalization, they face the challenge of maintaining high standards of reliability, security, and performance in their online offerings. This is where QA comes into play. By implementing robust QA processes, they ensure flawless user experiences across their platforms and mitigate associated business risks.
In this article, we’ll explore top fintech technologies and QA practices to enhance their quality.
Key innovations shaping fintech in 2024
As we continue into 2024, several transformative technologies are shaping the future of fintech:
- Generative AI (genAI)
Not all financial enterprises have managed to integrate their systems with genAI. That’s due to several complexities, including technical hurdles and the lack of accurate quality data.
However, those who successfully implemented genAI, reap several advantages. GenAI helps enhance efficiency and reduce costs through automating repetitive tasks, like data entry. This allows companies to save time and effort while minimizing the risk of human error, leading to more accurate results.
With GenAI, business can improve customer service through chatbots and virtual assistants, offering round-the-clock support and personalized recommendations.
And lastly, GenAI enhances risk management by analyzing a wide range of financial data, detecting suspicious activities, and preventing fraud and money laundering, thereby ensuring better security for financial institutions and their clients.
GenAI is predicted to explode in 2024 and allow companies to enhance operational efficiency, improve decision-making processes, and offer personalized services to customers.
- Robotic process automation (RPA)
Deloitte states that 53% of global organizations have already adopted RPA while 36% are planning to do it. That’s not surprising as RPA brings companies strong benefits: reduced costs, streamlined business workflows, increased productivity, and fraud prevention.
In the fight against financial crime, RPA enhances the speed and accuracy of fraud detection by automating due-diligence checks, sanctions screening, and transaction monitoring. By confirming data adherence to federal anti-money laundering guidelines and analyzing variances to flag potential instances of fraud, RPA bots bolster the cybersecurity infrastructure of financial institutions.
RPA helps fintech companies manage regulatory compliance by strengthening governance of financial processes. By automating manual tasks involved in reporting and consolidating data from various systems or documents, RPA streamlines the compliance process, reducing the risks of regulatory fines and reputational damage.
RPA also plays a key role in optimizing back-office functions in fintech, including transaction handling and data manipulation.
- Open ecosystems
To boost customer experiences and drive innovation, financial institutions are increasingly leveraging open ecosystems, including:
Open banking
Between 2023 and 2027, open banking transactions across the globe are projected to increase by 500%.
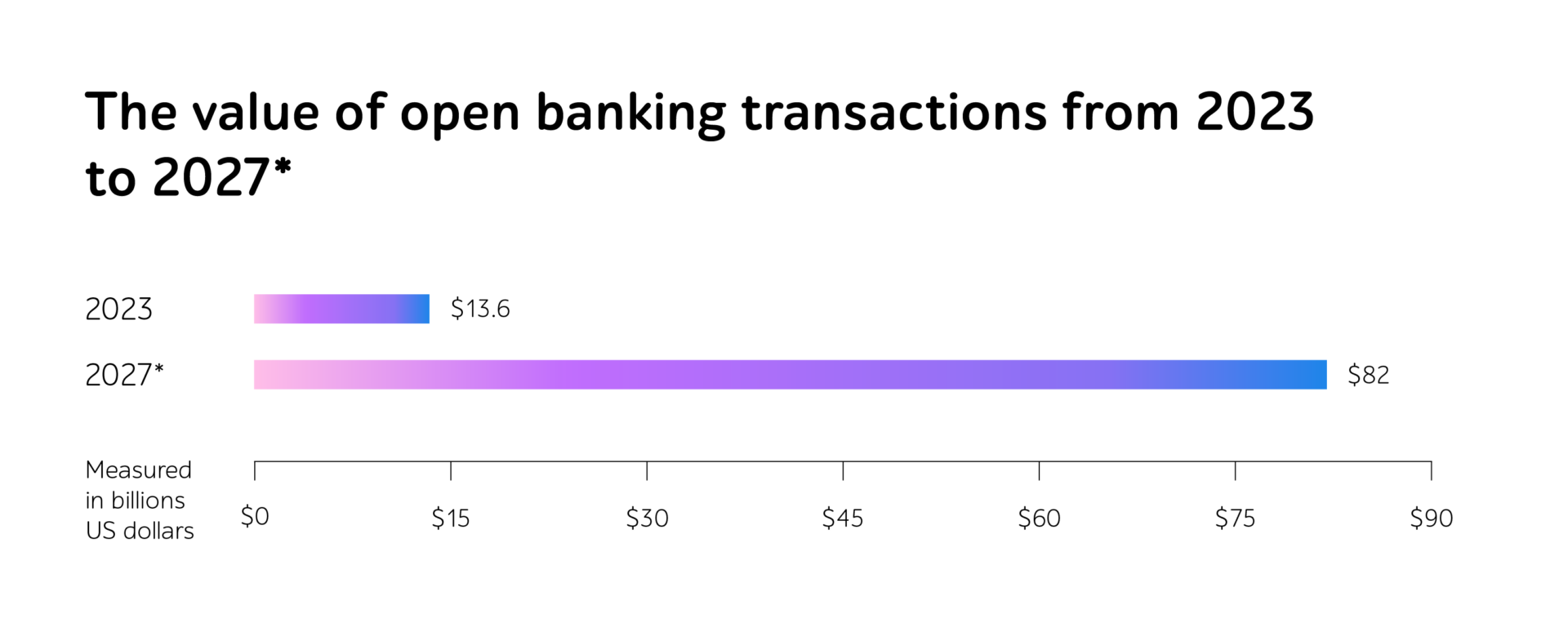
Source: Statista
Open banking revolutionizes the traditional banking model by fostering collaboration and interoperability within the financial ecosystem. Instead of being closed organizations, banks now offer limited access to customer data, enabling secure and electronic sharing with authorized third-party providers.
This paradigm shift empowers fintech businesses to leverage client information to enhance payment instruments, integrate user data into transactions, and provide a seamless payment experience. With open banking, customers can share their financial information securely, facilitating a unified flow for payments across different platforms and services without the need to switch between multiple applications.
Banking as a Service (BaaS)
BaaS operates on the principle of utilizing APIs to establish connectivity with clients. By leveraging the regulatory permissions of providing banks, BaaS end users can seamlessly integrate financial services without the need to navigate complex regulatory requirements.
This streamlined approach helps non-financial companies to create new solutions by incorporating a wide range of services, including deposits, money transfer, payments, currency exchange, and lending, into their offerings.
Embedded finance
It integrates financial services directly into non-financial ones to streamline the access to banking services for clients. Thus, users make payments, apply for loans, and access insurance services without reaching out to separate banking channels, gaining more convenience and accessibility.
- KYC, KYB, and AML solutions
KYC, KYB, and AML solutions play a vital role in addressing the escalating complexity of financial fraud in the fintech sector fueled by AI-driven techniques and deepfake technology. They are capable of real-time decision-making and continuous customer monitoring to verify users’ identities, assess business risks, and detect suspicious activities.
- Fintech regulators
Regulators worldwide are working diligently to address the modern risks of digital finance, particularly in areas, like cryptocurrency. As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, fintechs and other financial service providers should adapt quickly and confidently to keep up with new standards.
For instance, the top regulations in Europe are MiCA and PSD3. MiCA aims to provide a comprehensive regulatory framework for crypto assets, ensuring consumer protection and market integrity. Similarly, PSD3 seeks to enhance end-user rights and promote innovation in payment services.
QA to release high-end fintech software solutions
With banking applications handling sensitive financial data and facilitating billions of transactions, even the slightest system glitch or security vulnerability can have far-reaching consequences. Therefore, rigorous software testing should come to the forefront to ensure that fintech products meet the highest standards of reliability, security, and performance.
Below are presented testing types that are indispensable for banking applications.
- Cybersecurity testing
Cybersecurity testing for fintech software is imperative to safeguard sensitive financial information and protect against cyber threats and data breaches, especially in the context of open ecosystems. With the introduction of open APIs that transfer end-user details across various platforms, ensuring their safety comes to the forefront. It involves assessing the robustness of the software’s security measures and identifying vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Among the best practices, companies introduce penetration testing to simulate real-world cyber attacks and exploit vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and authentication flaws. These checks help identify whether it’s possible to gain unauthorized access to the system.
With vulnerability scanning, they scan the software for known fragilities, including outdated software components, misconfigured safety settings, and weak encryption protocols.
- Performance testing
Imagine that a fintech platform is experiencing latency issues during peak trading hours. Ultimately, it’ll lead to delayed transactions and payments, missed trading opportunities, and dissatisfied customers.
To avoid these and similar outcomes, financial businesses should implement performance testing. It helps assess the responsiveness, throughput, and resource utilization of banking applications under varying load conditions, ensure optimal performance, and enable fast transactions and data exchange.
- Functional testing
It assists in validating the software against requirements as well as evaluating the accuracy and reliability of financial calculations, transactions, and reporting functions while ensuring data integrity.
It plays a crucial role in testing the integrations of embedded banking into different products, such as eCommerce platforms or telecom services, by assessing how APIs function and interact within the BaaS framework.
It also includes testing account management, payment processing, and other critical features to verify that they perform as expected under different scenarios and conditions.
- Compliance testing
By focusing on compliance QA, fintech providers can ensure that their IT products adhere to regulatory frameworks and standards, such as MiCA, PSD3, GDPR, and PCI DSS. This is crucial to mitigate legal risks, safeguard data privacy, and boost customer experience.
Bonus: Blockchain testing
Blockchain testing helps companies check blockchain-based fintech solutions to ensure the integrity of transactions and identify and address potential vulnerabilities. It involves testing smart contracts for logic errors, assessing consensus mechanisms for robustness, and evaluating network performance under various conditions.
By conducting thorough blockchain checks, fintech companies can instill trust in their decentralized applications and foster adoption among users.
In a nutshell
The landscape of fintech is undergoing a profound transformation driven by modern innovations, including generative AI, RPA, and open ecosystems.
To ensure they meet high-quality standards, financial institutions can implement required QA practices: cybersecurity, performance, functional, compliance, and blockchain testing.
Planning to release banking software? Reach out to a1qa’s team to ensure its high-end quality.