QA’s role in adopting telecom trends for 2024
To maintain their competitive edge in 2024 and beyond, telecom companies have to stay ahead of emerging industry technologies. QA serves as a linchpin in this process, helping ensure the smooth implementation of innovations.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the key telco trends for this year and explore a QA strategy to launch high-quality telco software in an era of unprecedented change.
Navigating the trends reshaping telecom industry in 2024
Trend #1. 5G
Surpassing 1.5 billion connections by the end of 2023, 5G has firmly established itself as the fastest-growing mobile broadband technology of recent years. This statistic underscores the immense potential that 5G holds for transforming connectivity worldwide. By 2030, the GSMA professionals predict that 53% of the population will be using 5G, 35% — 4G, 8% — 3G, and 1% — 2G.
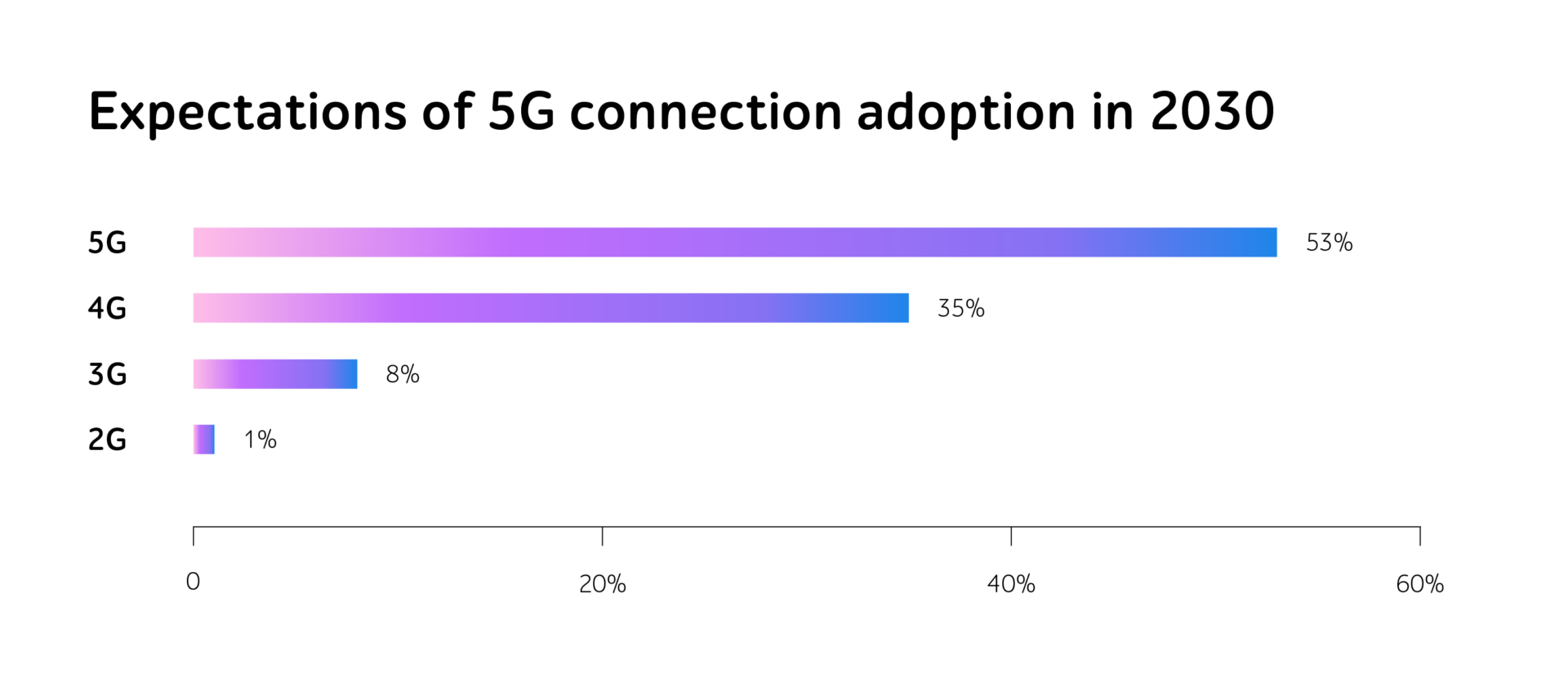
Source: The Mobile Economy 2024
The reach of 5G networks continues to expand across various regions from urban centers to remote rural areas while offering ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and high capacity.
Moreover, the advent of 5G is driving innovation in various industries. In healthcare, it facilitates real-time remote surgeries and high-definition video consultations between patients and healthcare professionals. In entertainment, 5G delivers immersive virtual experiences that allow users to enjoy multiplayer games with on-the-fly responsiveness and minimal lags.
As the adoption of 5G-enabled devices and services continues to grow, telecom companies should focus on ensuring seamless network performance, smooth operation of mobile and web applications and computing centers, and strong security to provide customers with the full potential of 5G technology.
Trend #2. Broadband connectivity
2024 marks a significant milestone in the expansion of broadband connectivity. Consumers are witnessing a proliferation of options for accessing the high-speed Internet driven by advancements in terrestrial wireline, terrestrial wireless, and satellite technologies.
Nowadays, Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) and Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite Internet are gaining momentum, particularly in remote regions. These technologies help offer viable options to traditional wired broadband services, bridge the digital divide, and extend access to previously inaccessible areas.
Trend #3. AI-driven solutions
AI-driven solutions are now becoming increasingly prevalent in the telecommunications industry, enabling operators to:
- Optimize network performance. By adjusting routing protocols and network topologies, AI-powered networks can adapt to changing conditions and traffic loads, ensuring consistent user experiences.
- Enhance cybersecurity. By analyzing network traffic patterns and identifying suspicious behavior, AI-driven security systems can proactively mitigate cyber attacks, protecting sensitive data and infrastructure from harm.
- Deliver personalized services to clients. By leveraging customer data and behavioral insights, AI helps telecom companies tailor service offerings and recommendations to individual preferences, increasing their loyalty and receiving more revenue opportunities. What’s more, with AI seamlessly integrated into chatbots and personalized AI assistance, they can elevate their client support. AI-driven networks enable efficient problem-solving and service sales without human intervention, minimizing operational expenses.
- Ensure predictive maintenance. With AI at the core, telcos continuously monitor the state of their equipment, analyzing statuses and identifying anomalies in network performance. By leveraging AI algorithms, they proactively resolve issues before they impact customer experience, reducing downtime and enhancing overall reliability. This data-driven approach allows them to predict potential failures and take proactive measures to address them with the hardware, including cell towers, power lines, and servers in data centers, ensuring seamless operations and uninterrupted service delivery.
Driving successful adoption of telecom trends with the help of QA
QA is indispensable to ensure the successful implementation of telecom trends and the reliability of IT products. Let’s explore key testing types, helping deliver high-quality telco software.
All tests can be devided into two groups:
- Functional and non-functional testing
Performance testing
Performance testing holds a pivotal role in guaranteeing the seamless operation of critical systems responsible for delivering telecommunications services. By meticulously subjecting telecom solutions to stress and load tests, companies can ascertain whether they are able to promptly respond to a myriad of subscriber requests. This involves scrutinizing both client- and server-side functionalities, ensuring that vital components, such as billing and CRM systems, efficiently receive and process requests.
Performance checks help telco operators release highly reliable software while delivering exceptional user experiences and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Functional testing
Functional testing ensures that all features of telecom products work as intended. It extends to verifying applications designed for customers, user support systems (chatbots or live chats with operators), back-end software for telecom, data centers, CRMs, ERPs, and additional services (media streaming platforms).
This involves testing various scenarios, inputs, and outputs to verify the correct behavior of the software. For instance, validating the functionality of invoicing processes.
As part of functional testing, UAT helps ensure the seamless integration of new systems, modules, or integrated solutions within telecom businesses. While traditionally associated with third-party integrations, UAT testing extends beyond this scope to encompass newly developed systems or modules as well.
The aim of UAT is to validate business requirements, verify functionalities, and assess user experience across various applications and platforms. For instance, in the integration of self-service portals and mobile apps, UAT testing enables QA teams to simulate real-world usage, such as managing accounts, viewing usage details, and paying bills. Additionally, it allows verifying the usability, performance, and security measures implemented to protect customer data and transactions.
Security testing
Security testing is paramount to safeguard sensitive customer data and safeguard against cyber threats, considering the extensive network and cloud infrastructure involved. Telecom companies should be highly vigilant about potential data leakage and breaches, as they handle end-user financial and personal information. Moreover, with numerous entry points into telecom networks, including interconnected software, like CRMs, billing, and operational systems, comprehensive security testing is a must-have.
By conducting penetration testing, businesses simulate real-world attacks to identify potential weaknesses in telecom systems, such as weak authentication mechanisms or exposed network ports.
To uncover entry points for cybercriminals and assess the safety posture of telco infrastructure, companies can introduce vulnerability scanning tools, including Acunetix, Burp Suite, and Nessus.
Test automation
Telco providers can automate any tests, but it’s more profitable to automate repetitive test scenarios, reducing manual effort and accelerating the QA workflow.
To enhance testing coverage and efficiency, telecom providers leverage automated regression testing. By automating test processes, companies perform more tests in less time, significantly boosting coverage and accuracy while neutralizing the risk of human errors. These automated scripts can be reused repeatedly, optimizing overall testing efforts and ensuring comprehensive coverage across software updates, patches, and configuration changes.
- Testing based on the product type
OSS/BSS testing
As OSS and BSS form the backbone of telecom services, it’s mission-critical to enable their seamless running. OSS/BSS testing encompasses a range of QA activities tailored to validate the functionality, reliability, security, and performance of telco systems, which are responsible for key functions, involving billing, customer management, and network operations.
With OSS/BSS checks, businesses also verify the accuracy of billing calculations for various service plans and validate the CRM system to make sure that customer information or service requests are accurately captured and processed.
Migration testing
It’s imperative to test the data and readiness of the system before moving to new OSS/BSS systems, such as billing or CRM platforms. This process involves migrating and validating large volumes of data to ensure seamless integration and prevent disruptions to routine subscriber activities. Additionally, it’s necessary to address security vulnerabilities and optimize performance to uphold uninterrupted subscriber activities.
Cloud testing
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in modern telecom operations, enabling companies to scale resources up and down, such as networks and servers, as well as storage on-demand. Leveraging cloud infrastructure, telecoms can keep and process vast amounts of user data remotely, ensuring cost efficiency and global reach.
Therefore, businesses can introduce cloud testing to assess the reliability, scalability, and security of telecom products delivered through cloud infrastructure.
With cloud tests, operators can also confirm the security posture of cloud-based telecom solutions, including data encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards.
To conclude
The telecommunications landscape is continuously evolving. 5G, broadband connectivity, and AI-driven solutions are set to redefine this sector in 2024.
To implement these trends with confidence and assurance, businesses can encompass a comprehensive QA strategy that involves performance, functional, OSS/BSS, migration, UAT, cloud, security, and automated testing.
Reach out to a1qa’s team to get support in ensuring the high quality of your telecom software.