Reaching HIPAA compliance for eHealth solutions through QA
With the advent of advanced tech, healthcare institutions have leaped forward in embracing a digital mindset to transform and enhance relationships with patients. By applying innovations such as AI, VR, 3D printing, gene editing, and many others, medical establishments revolutionize their approaches to care delivery and prolong our life expectancy.
However, when applying this state-of-the-art software, healthcare employees use personal patients’ data more than ever before relying on health conditions and previous disease records. This is why while developing digital clinical assistants, we suggest making sure they comply with standards and don’t cause any harm.
Among the most pervasive regulations in healthcare, HIPAA stands out ― The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. Aiming to defend sensitive patients’ data, every eHealth solutions developer tends to follow these inviolable safety obligations.
In the article, we bring to notice the HIPAA benchmarks and shed light on the strictly required data security aspects that aim to provide patients with greater control over their personal data and ensure its full protection. Furthermore, we appraise how QA and software testing services can help comply with the established norms.
Standards: regard or disregard…
Due to being among life-threatening industries, healthcare doesn’t excuse any errors. Even a minor one can trigger critical consequences for human well-being. Let’s say an unintentional misprint in prescriptions may cause inappropriate treatment or no treatment at all. Inaccurate medical equipment setup can implicitly affect the health state. If not mentioning negative scenarios that may occur when compromising on software quality and not adhering to requirements.
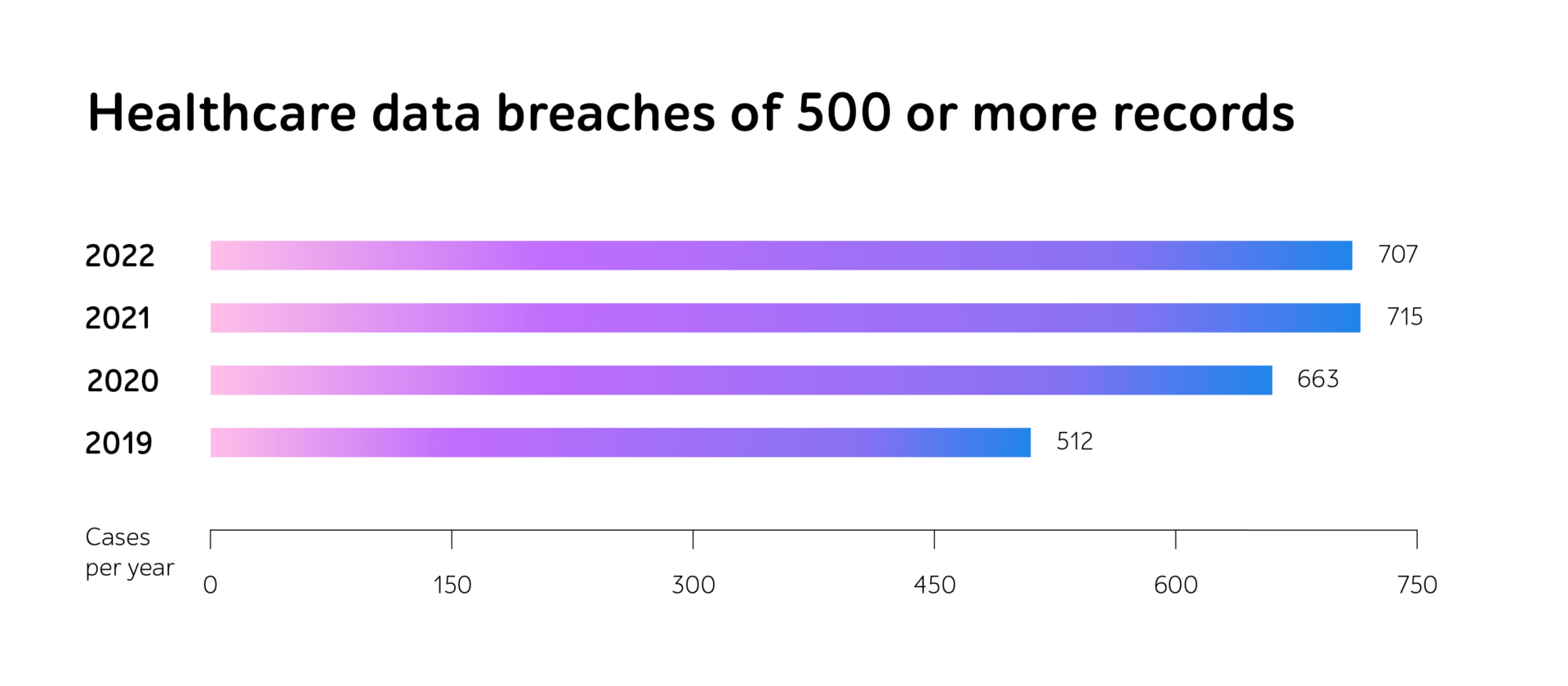
As it’s a mandatory step of verifying eHealth solutions’ functionality before going live, the HIPAA community sets penalties for violations of the regulations. In 2022, alongside a substantial increase in fines, reaching $60,973 only for a minor violation, the number of breach cases has also grown.
Moreover, businesses with 500 and more individuals impacted by leaks get to the Breach Notification Portal, known as the “Wall of Shame,” severely tarnishing the company’s reputation and reducing patients’ loyalty.
Shifting to digital document storage and management, information protection is gaining a greater priority. Businesses should implement safety measures, as private data might turn to the object of cyber attacks and inappropriate data usage. HIPAA Journal indicates the number of malicious actions is only soaring within years. In total, around 50 million Americans were affected by health data leakage in 2022.
Following three of HIPAA’s cornerstones
Within this eHealth law’s legal force, every organization and its partners that perform whatever activity over PHI undertake to comply with the Act’s requirements. It begs the question, what are those rules eHealth solutions should coincide with?
Despite the norms’ intentional vagueness, sensitive information keepers should take the digital, material, and managerial guarantees into work, as well as risk evaluation and ways of eliminating information breaches’ consequences.
Let’s get a more detailed grasp of each HIPAA’s basic pillar, helping provide PHI integrity and complete privacy.
1. Technical safeguards
Hacking and IT incidents are now the foremost means of data security violations. Though organizations are now much better trained to expose malicious usage, the number of cyber attacks is only increasing. By 2022, it reached 707 cases in a year.
Intended to protect PHI, digital regulations assume data encryption whether it transfers within a company, moves outwards on an organization’s internal firewall servers or is kept in storage. Hence, if the data falls into the hands of fraudsters, they won’t be able to read, decipher, and harness personal details.
While encryption is becoming a mundane phenomenon, HIPAA proposes to adhere to the following standards to defend the data:
- Access control – providing access to electronic PHI only to authorized individuals and preventing unauthorized penetration.
- Audit control – recording all actions related to electronic PHI, such as deleting or changing data in the electronic medical card.
- Integrity – ensuring the consistency of stored information and eliminating its destruction by unauthorized users.
- Person or entity authentication – verifying that the authentication process goes smoothly.
- Transmission security – checking the encryption and safety of the electronic PHI delivery methods.
2. Physical safeguards
Moving beyond the online space, organizations should keep all kinds of devices leveraged to access PHI safety. They opt for various scenarios of storing data, and have to be well-secured to avert unsolicited information usage. On-premises, cloud, or rented servers ― it’s no matter.
So, HIPAA material protection measures include 4 enforcing regulations:
- Facility access controls – restricting physical access to PHI.
- Workstation use – eradicating a possible negative impact and security risks related to the workstation’s surroundings.
- Workstation security – adopting physical protection to all workstations that possess access to PHI.
- Device and media controls – verifying the transfer, removal, and reuse of electronic media, containing PHI.
3. Administrative safeguards
One more pivotal aspect of a HIPAA compliance checklist is risk regulations. This area is under the most thorough control, which is held continuously to ascertain the company’s holistic and sustained risk management. To meet the norms, HIPAA’s specialists recommend complying with a set of standards to evaluate the already existing safety measures and analyze possible hazards.

QA as an accelerator of suiting HIPAA’s checklist
The development and digital life of any IT solution are speeding up with years. Due to heavy competition in the market and high user expectations, companies are to release reliable software at short notice.
As for eHealth products, companies should consider their potential functioning failures with particular emphasis. Quality assurance can be a powerful way to eradicate them, ensure flawless operation, and meet all the safety requirements.
Security testing lays in the heart of getting HIPPA compliance, as its main purpose is to ensure data privacy and end-user confidence in the application. Penetration testing is the most progressive and topical approach to derive these results. Acting like real hackers, the specialists may identify the bottlenecks in advance, so they can decrease chances of cyber incidents.
Since medical software products often receive updates and new components, it’s crucial to continuously track that they do not contain any vulnerable points. As this is a time-consuming activity, businesses adopt test automation to speed up regression checks and deliver a high-quality IT product to the market on time.
However, HIPAA compliance is not the only thing that indicates that an eHealth solution operates well and satisfies customers’ needs. Noteworthy is looking at the application from various angles to ensure its comprehensive and smooth work. As there’s no one-size-fits-all QA strategy for every project, specific business demand and objectives speak volumes about an appropriate QA package.
But companies may choose full-cycle testing, a one-stop QA measure that helps determine the necessary testing types performed during all the SDLC steps. It can include functional and compatibility testing or mobile and performance testing, or others that suit the project’s goals. Thus, one might be confident in the software quality and avert any kinds of defects in the go-live stage.
Taking an example, a1qa’s team provided all-embracing QA support, including assistance in HIPAA compliance, to a developer of the wellness portal and mobile apps. In addition to getting ready for passing HIPAA certification, the QA specialists performed thorough functional and compatibility testing, as well as test automation. Thanks to this, the solution under test successfully underwent the security and privacy control and featured total data protection.
In a nutshell
Within the healthcare industry’s gravity, standards compliance has become an integral part of medical software development.
According to HIPAA regulations, any eHealth solution should comprise technical, physical, and administrative safeguards as well as continuous maintenance.
To ensure medical IT products’ release and attain high quality and complete privacy, businesses should consider software testing as an inalienable SDLC step. By applying a need-driven QA bundle, you can meet desired outcomes and enhance customer satisfaction within tight deadlines.
Need support in eHealth software testing? Reach out to us to get a consultation with our QA experts.