The ultimate QA guide for smoothly migrating to Web 3.0
The global Web 3.0 market size is projected to reach 81.5 billion by 2030 — we are witnessing how organizations shift smoothly from Web 2.0 to its advanced version, Web 3.0. But what is Web 3.0, and how is it practiced in today’s world?
Within Web 3.0, companies offer AR spaces and virtual worlds for holding meetings, providing medical care, educating, and socializing. For example, in 2021, Nike opened a Roblox-based showroom and has attracted almost 7 million consumers since its release.
However, as Web 3.0 products are highly sophisticated, businesses should take exceptional care about their quality.
In this guide, explore the benefits companies attain with Web 3.0 as well as 4 testing types that allow moving flawlessly to Web 3.0.
Migrating to Web 3.0: benefits to reap
Combining a range of novel technologies, including AI, ML, IoT, and blockchain, Web 3.0 promotes better human interaction and improved user experiences within dimensional worlds.
Compared to Web 2.0, primarily characterized by a multitude of cyber hazards, lack of proper security, and total control by large companies, Web 3.0 brings more powerful benefits for both organizations and users. Let’s take a closer look at 5 of them.
1. Enhanced privacy
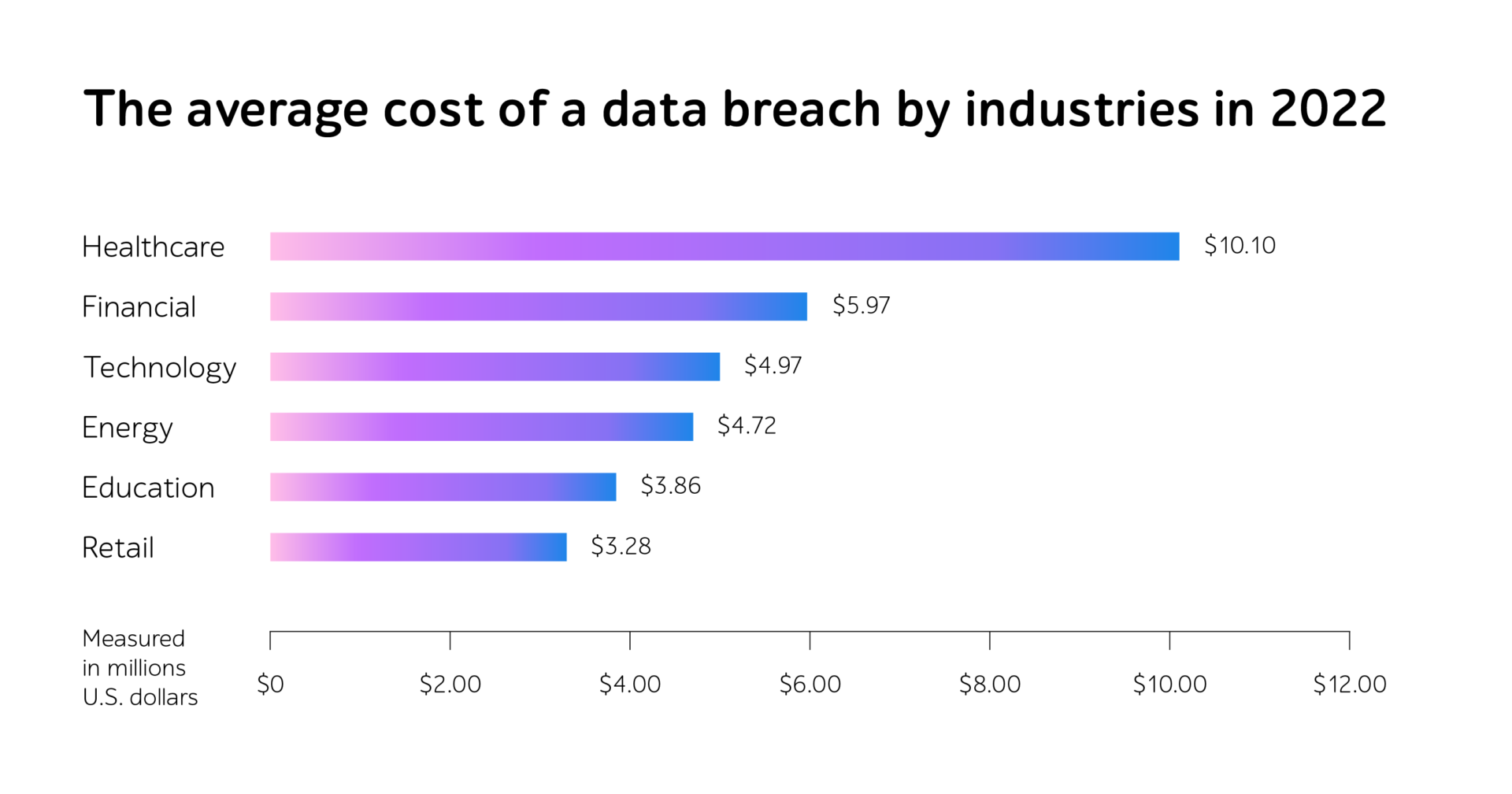
One of the alarming issues with Web 2.0 is the lack of safety, resulting in digital threats such as cryptojacking, DDoS, SQL injection, malware, DNS tunneling, and man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM). It certainly has a detrimental effect on the company’s reputation and depending on the industry, the average cost of a data breach may vary: for healthcare, it reaches $10.10 million, for financial — $5.97 million, and for technology — $4.97
In July 2022, hackers stole personal data (social account and property information, addresses, policy numbers, bank reports) from KeyBank’s customers via a third-party insurance vendor. The damage totaled $5 million. This can probably highlight the pivotal role of comprehensive software testing to verify the security policies and tools of both the organization and its providers.
Due to the decentralized nature of Web 3.0 and embedded blockchain mechanisms, hackers find it much harder to penetrate the network.
2. Customized experience
Web 2.0 is filled with intrusive advertising that does not always meet the needs of end users, pushing them away. AI algorithms of Web 3.0 allow detecting end-user preferences, adapting to them, and providing personalized offers.
3. Data ownership
Nowadays, global corporations, like Facebook, Microsoft, or Amazon, collect consumers’ personal data to sell it to advertisers, making billions on it.
Comparing Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0, the latter allows end users to become the only owners of their sensitive information, choosing who to grant access to.
4. More efficient search
Today’s search engines don’t always operate smoothly and don’t always deliver the right results. As an integral part of Web 3.0, the semantic web doesn’t focus on keywords, but on the meaning of words and on the digital context. This helps users to easily find necessary information as the web pages are better sorted.
5. An advanced immersive experience
Immersive capabilities erase the boundaries between the physical and virtual worlds. AR/VR technologies create new ways of interacting with people, goods, and services.
For instance, due to Web 3.0, 95% of healthcare organizations provide patients with distant assistance, which is twice as much as it was before 2020.
eCommerce companies can also offer their buyers a unique shopping experience regardless of their location, which means an expanded client base and more profits.
A comprehensive QA guide: migrate to Web 3.0 with confidence
As the metaverse, AR/VR technologies, blockchain, and Web 3.0 products are intertwined, it’s crucial to apply the most suitable QA strategy. We suggest following a QA guide that includes cybersecurity, performance, accessibility, and usability testing to smoothly move to Web 3.0 and deliver high-quality software to end users.
1. Cybersecurity testing
Since Web 3.0 is a complex concept, checking the security of its core aspects is a must.
It’s vital to conduct penetration tests, vulnerability assessment, and social engineering, helping simulate attacks and identify bottlenecks that can tarnish reputation and affect customers.
Being an intrinsic part of Web 3.0 software products, blockchain transactions can also be exposed to malicious attacks and viruses, thus requiring the early detection of loopholes. The lack of security measures may result in large financial damages, like what happened to the cryptocurrency exchange Bithumb which lost around $30 million in coins as well as the customer’s trust.
2. Performance testing
High speed, stability, and scalability are top priority aspects for today’s applications, and the same is true for Web 3.0 solutions. According to a survey by Unbounce, 70% of consumers said that page load speed affects their decision to purchase items.
The same scenario can be prevented by introducing performance testing. Try to imagine how many people can connect to a metaverse, but the question is, can your solution handle that load? In order for Web 3.0 apps (especially for AR and VR) to operate like clockwork, the company needs to identify all possible latency issues and ensure high speed, stability, responsiveness, and scalability of the software under both normal and overload conditions.
3. Accessibility testing
Since most Web 3.0 solutions combine virtual, augmented, and physical reality, companies should analyze from the ground up if people with disabilities can easily use them.
Therefore, organizations should ensure that the app offers special features, like captions and audio/video hints to provide an inclusive and easy to navigate IT solution for absolutely all customers.
By applying accessibility testing fulfilled in accordance with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines and other standards, companies verify whether:
- The alternative movement and control methods work properly
- Consumers with eyesight impairments can perceive visual elements and available content
- The headset triggers discomfort for certain groups of users (e.g., those who wear glasses).
4. Usability testing
If the Web 3.0 software product is too immersive, it may cause negative experiences, like motion sickness, eyestrain, headaches, and fatigue.
To deliver an intuitive and user-friendly app, companies apply usability testing. This helps identify virtual and physical balance, problems related to the end-user interaction, and failings, such as players falling through windows or getting stuck in other objects.
To put it short
Migration from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 helps businesses enhance privacy, customize end-user experience and provide data ownership, efficient searching, and advanced immersive engagement.
Adhering to a QA guide, embracing cybersecurity, performance, accessibility, and usability tests, may assist organizations in releasing competitive Web 3.0 solutions and delivering a flawless digital experience to consumers.
When you are ready to boost your Web 3.0 software product quality, contact a1qa’s team.