Using back-to-back testing in the telecom industry
First, let’s have a “helicopter view” on what comparative test provides and which cases are appropriate for back-to-back in Telecom industry.
Most commonly, comparative testing is used in the case of the full replacement of OSS/BSS solution, which is absolutely crucial for any Telecom business. Rarely, new version of existing OSS/BSS is installing and requires verification.
Comparative testing checks two identical OSS/BSS with the same input data in order to reveal incorrect data processing.
Three main goals to use comparative tests
- Detection of functional defects in Rating and Billing systems;
- Detection of migration errors when user data transferred from one system to another;
- Configuration defects identification (setting tariffs in both systems).
The general workflow for comparative test (proposed by the author while implementing projects in Telecom) is shown at the picture below.
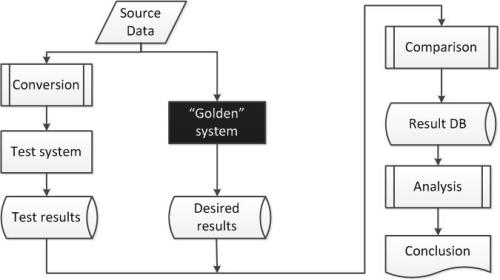
As you can see, two identical systems are required for the testing process: the master (“Golden”) and the test system itself.
Sometimes the input data for “Golden” system cannot be accepted by the test system without additional pre-processing. Then, test data must undergo further conversion phase for compatibility with the test system. After getting results from both systems, they have to be compared – the essence of comparative test – that is, as a rule, an automated process implemented independently from environments. The final step is an empirical data analysis activity that is performed by the tester.
When we analyze the efficiency of comparative test regarding OSS/BSS solutions on real Telecom projects, we must have a critical view and list some of the shortcomings:
- The test involves a lot of empirical work, which is difficult to automate (final stages of divergence analysis are performed manually).
- During late iterations of the test, a lot of records with numerical discrepancy that cannot be considered as defects can be revealed. These records must be filtered from comparison
- Sometimes the test indicates good results while in reality the situation is bad. For instance, during the collection of final statistics, two critical defects might neutralize each other when one of them increases and the other decreases the final amount.
- Completely relevant comparative test should be performed for at least one full billing period (about one month), which is not usually the case as the test lasts less than 30 days.
As for the billing systems comparative tests requires achieving a sufficiently high level of coincidence of the output results for both systems (for instance, 99.99%). Achieving this result is a bit tricky, due to the following factors:
- Different rounding of floating-point data in two systems;
- Incorrect development of mapping tables (service A in the system 1 corresponds to service B in the system 2);
- Different order of records processing in two systems may lead to divergence in tariff discounts application;
- Peculiarity of some data types in database (example – rating results for call forwarding);
- Dynamism of the master (“Golden”) environment. In the real life, clients are frequently changing tariff plans, phone numbers, SIM-cards, contract statuses etc. It’s almost impossible to synchronize all these changes in the test system;
- Confirmed changes in business-logic, that is the differences in behavior between the two systems envisaged by Telecom operator requirements to the new system;
- Uncertainty and indistinctness of the system requirements;
- Inability to implement the requirements of the system under test.
All these factors lead to numerical discrepancies in the results, which may be up to 25% from reference values.
Nevertheless, based on my experience I would advise implementing back-to-back testing due to the many advantages that this method provides:
- High level of test coverage for the system;
- The opportunity to get additional metrics of the system quality;
- Availability of implementing migration and configuration tests, not only functional tests;
- High automation level of the testing process.
This is confirmed by the picture below illustrating results of several testing iterations on a real Telecom project.
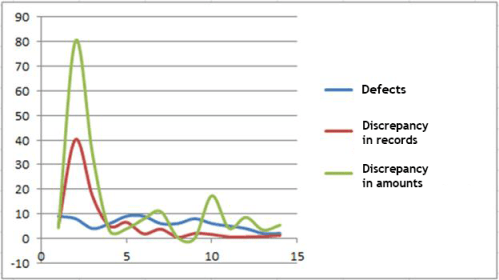
These statistics contains three metrics:
- Defects – the number of functional, integration and configuration defects in the test system
- Discrepancy in records, % – the percentage of data units which gave different output results, relative to the originally loaded amount
- Discrepancy in amounts, % – the ratio of the total discrepancies amount between the master and the test system relative to the total amount of charges in the master system
Conclusion
We can note high efficiency of this type of test in relation to OSS/BSS. A good practice is to use a back-to-back test together with other traditional strategies for testing, since they are not mutually exclusive and able to detect defects of different classes of the same functionality. You should also keep in mind that an adequate strategy must be developed for back-to-back tests, taking into account all advantages and shortcomings presented in the article.
The article was published at SoftwareTestingMagazine.